Ergonomics
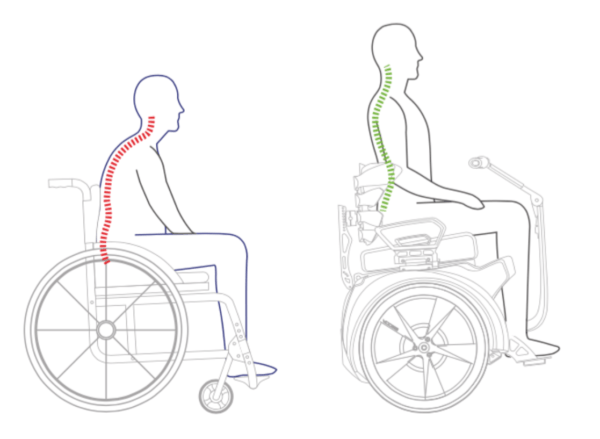
The movements of the upper body cause the Seated Segway to start moving or to stop again, thus enforcing an upright and active sitting position. In contrast to a regular wheelchair, in which a static and bent position is common, the body is stimulated to actively use the muscles in the trunk. The trunk is stretched upwards and is actively in motion while driving.
Active upper body movement
Due to the active movements, the muscles are continuously addressed and trained, even muscles whose nerves are not active. This results in a better blood circulation, in addition, an activation of the digestion takes place. While using the Seated Segway, the pressure distribution on the seat also varies, so that a better blood circulation takes place here too, which can even prevent pressure ulcers.
Injury prevention
Because weight transfer from the upper body is used as the drive in a Seated Segway, the arms are only used to operate the steering wheel. As a result, there is no load on the arms and shoulders and known structural injuries are prevented. Shoulder complaints in particular are a major problem among wheelchair users, resulting in a lot of pain and sometimes even surgical interventions. Using a Seated Segway can prevent these problems. In addition, a Seated Segway is an ideal aid to use in rehabilitation or recovery.